Fachbereich Physik

(the PEEM at work)
|
Fachbereich Physik |
|||
| Magnetic imaging by photoelectron emission microscopy (PEEM)
|

(the PEEM at work) |
||
See
also: Research topics of AG Kuch at Freie Universität Berlin
See
photographs of the previous group at MPI Halle
The magnetization
reversal of magnetic microstructures can be followed
with the PEEM by applying short magnetic field pulses between
the acquisition of domain images. Interesting domain configurations
are observed in triangular microstructures. The magnetic coupling
at the interface between an antiferromagnetic and a ferromagnetic
layer is of highest fundamental and technological importance
due to the phenomena encountered ("Exchange Bias"). Single crystalline
bilayers of Co (ferromagnet) and FeMn (antiferromagnet) can be grown
on Cu(001). Magnetic imaging revealed stunning changes in the as-grown
domain patterns when at the paramagnetic/antiferromagnetic transition
of the FeMn layer. Taking advantage
of the element-selectivity of the method, different magnetic
layers in a multi-layered magnetic sample can be imaged separately
at the same position. This allows to identify micromagnetic mechanisms
coupling two magnetic layers that are separated by a non-magnetic
spacer layer.![]()

Magnetic circular
dichroism (XMCD)...
...is used as element-selective
magnetic contrast mechanism for the magnetic imaging in PEEM.
XMCD is the dependence of x-ray absorption on sample magnetization
direction.
More...
![]()

Magnetization reversal in magnetic microstructures
More...
![]()
![]()

Bilayers of antiferromagnetic and ferromagnetic films
More...![]()
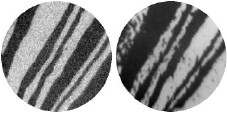
Layer-resolved magnetic microscopy
More...![]()
![]()
|
Microspectroscopy:
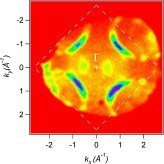
Fermi surface mapping The PEEM can not only be used to display magnified images of the sample surface. When the projection lenses are set to display the focal plane of the objective lens, the angular distribution of the emitted electrons is obtained. This can be used to display two-dimensional photoelectron angular distribution patterns and perform, for example, Fermi surface mapping. More... |

|
Microspectroscopy:
Magnetic contrast from photoemission When energy filtering of the imaged electrons can be performed, additional contrast mechanisms besides XMCD can be used for magnetic imaging. Magnetic contrast can be obtained taking advantage of magnetic dichroisms in angle resolved photoelectron spectroscopy. More... |
|
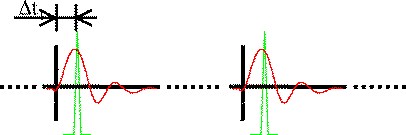
Time-resolved magnetic
domain imaging Stroboscopic time-resolved measurements can be performed by synchronising short magnetic field pulses to the time structure of the synchrotron radiation, which is delivered in short pulses. We present the first time and layer resolved magnetic imaging studies of magnetization reversal dynamics, using trilayered magnetic spin-valve systems as samples. More... |
E-mail comments and questions to kuch@physik.fu-berlin.de.
Last update: 28-Aug-2003
back to top