Publications:
Applied Physics A 76, 665 (2003),
Physical Review B 67, 214403 (2003).
Taking advantage
of the element-selectivity of XMCD as magnetic
contrast mechanism, different magnetic layers in a multi-layered magnetic
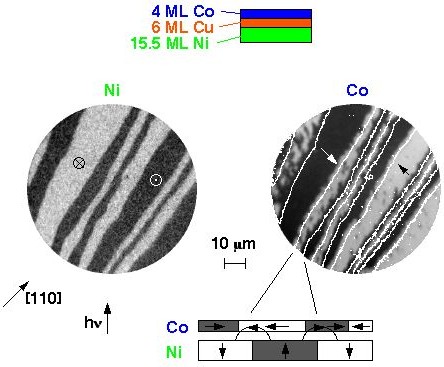
sample can be imaged separately at the same position. The images show the
magnetic domains in a Co/Cu/Ni trilayer on Cu(001). The left image shows
the domains in the Ni magnetic layer, the right image the domains of the
Co magnetic layer at the same position. Both layers are separated by a non-magnetic
Cu spacer layer. Because of magnetic
anisotropies, the magnetization direction is out-of-plane in the Ni layer
and in-plane in the Co layer. The domain patterns nevertheless show a striking
similarity. For better comparison the positions of the Ni domains are reproduced
by white lines in the Co domain image. The correlation
is explained by local magnetostatic fields from the boundaries of the magnetic
domains of the Ni layer, the domain walls, as schematically shown below
the images. A domain pattern in the Co layer which reproduces the striped
Ni domain pattern at shifted lateral positions is energetically favorable
because it minimizes the Zeeman energy. The study of such
local, micromagnetic coupling mechanisms between ultrathin magnetic layers,
a subject of highest technological and fundamental importance, is at the
leading edge of current magnetic thin film research.